By Chef Peter | Expert Chef Nutritionist | December 11, 2025
⏱️ Prep Time: 30 seconds | 🔬 Evidence Level: Mixed (Digestive benefits proven, ED claims unproven)
💰 Cost: $0.10 per serving | ⚠️ Safety: Safe in moderation, risky in excess
Perfect for: Understanding viral health claims, learning safe baking soda tonic recipes, exploring alkalinity benefits for digestion and inflammation, and discovering what actually works versus marketing hype.
Three months ago, a patient named Michael, 52, walked into my nutrition consultation clutching his phone showing a viral video about a “30 second hard tonic with pure baking soda” promising to cure erectile dysfunction in 30 minutes. He’d already been mixing baking soda water daily for two weeks based on social media claims, experiencing stomach upset and disappointment when promised results never materialized.
“Chef Peter, I watched dozens of videos saying this baking soda ed tonic would change my life,” Michael told me, frustrated and confused. “Some add apple cider vinegar, others lemon juice, and everyone claims it’s scientifically proven. But I feel worse, not better, and nothing’s improved sexually. Did I do something wrong?”
Michael’s experience represents thousands of men (and women) caught between viral health trends and evidence-based nutrition science. The “30 second hard tonic with pure baking soda” has exploded across social media, YouTube, and health forums with extraordinary claims about erectile dysfunction, sexual performance, weight loss, inflammation reduction, and metabolic enhancement—but what does the actual science say versus the marketing hype?
Over my 15+ years as a chef nutritionist specializing in therapeutic nutrition and baking soda-based health protocols, I’ve watched countless “miracle remedies” emerge, gain viral traction, then fade when reality fails to match promises. Baking soda tonics represent a particularly interesting case—they contain genuine health-supporting compounds with documented benefits for specific conditions, but they’re also wrapped in exaggerated claims about sexual performance that have zero scientific support.
This comprehensive guide cuts through the confusion with evidence-based information you won’t find in viral videos or competitor articles. We’ll examine what the 30 second hard tonic actually is and its various formulations, the truth about baking soda and erectile dysfunction claims (spoiler: there’s no evidence), what baking soda tonics CAN actually do for digestion, inflammation, and alkalinity, safe recipes including apple cider vinegar and baking soda tonic, baking soda lemon tonic, and acv baking soda lemon and manuka honey tonic variations, proper dosing and timing protocols, potential risks and who should avoid these tonics, and most importantly—the nutritional optimization strategies that address root causes of the health issues these tonics claim to fix.
Whether you’re searching “tonic for ed with baking soda” hoping for breakthrough solutions, researching “baking soda tonic benefits” for general wellness, or simply trying to separate fact from fiction in viral health trends, this article provides the honest, comprehensive information you need to make informed decisions.
What Is the 30 Second Hard Tonic With Pure Baking Soda?
The “30 second hard tonic with pure baking soda” refers to a viral health remedy involving mixing baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) with water and drinking it quickly—preparation takes about 30 seconds. The term “hard” in various viral marketing materials suggests claims about erectile function improvements, though as we’ll explore, these specific sexual performance claims lack scientific support.
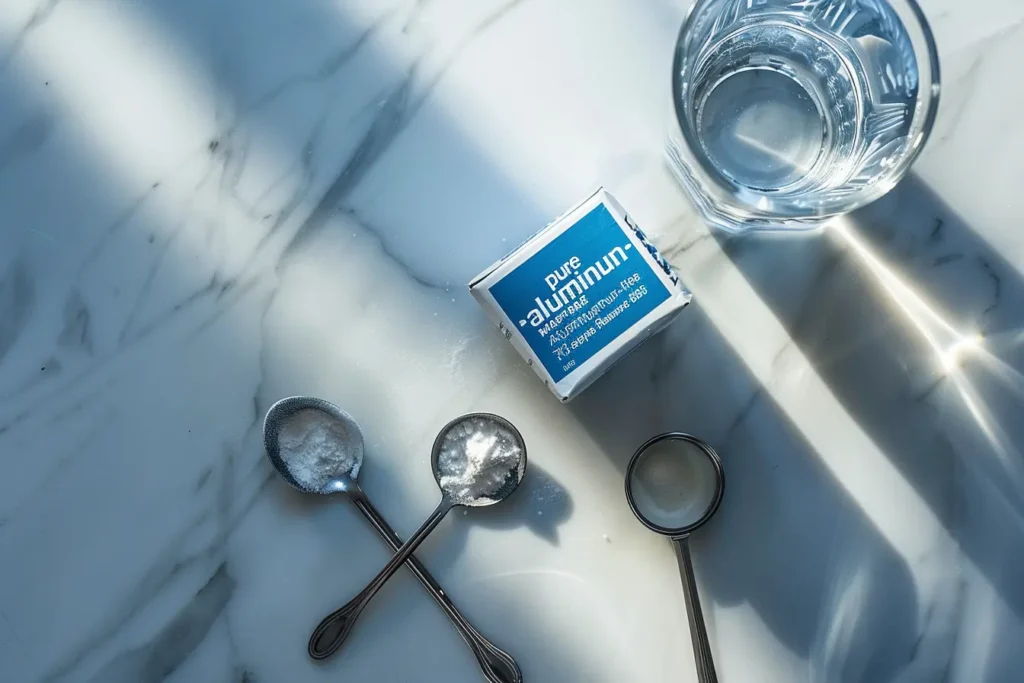

The basic baking soda tonic recipe consists of 1/4 to 1/2 teaspoon baking soda dissolved in 8 ounces water, stirred for 20-30 seconds until fully dissolved, and consumed immediately. The alkaline solution (pH typically 8.0-8.5) neutralizes stomach acid quickly and enters the bloodstream within minutes, creating the systemic alkalinity proponents claim provides various health benefits.
Multiple variations of this “30 second” tonic exist across health forums and social media including: pure baking soda and water tonic (the simplest version), apple cider vinegar and baking soda tonic (combines acidic ACV with alkaline baking soda creating fizzy reaction), baking soda lemon tonic (adds citric acid and vitamin C), acv baking soda lemon and manuka honey tonic (comprehensive version with multiple functional ingredients), and morning tonic with baking soda (timing-specific protocol claiming enhanced benefits on empty stomach).
The viral marketing around these tonics, particularly the “ed tonic with baking soda” claims, typically makes several extraordinary promises: erectile dysfunction improvement or cure within 30 minutes to days, enhanced sexual performance and libido, rapid weight loss and belly fat reduction, inflammation reduction throughout the body, metabolic enhancement and energy increases, and pH balance leading to disease prevention. However, as we’ll examine in detail, scientific evidence supports only some of these claims while others remain completely unsubstantiated or disproven.
From my nutritionist perspective working with clients like Michael who’ve tried these viral remedies, the most critical issue isn’t that baking soda tonics are inherently dangerous (they’re generally safe in appropriate amounts)—it’s that exaggerated marketing creates false hope for serious medical conditions like erectile dysfunction while potentially delaying proper medical evaluation and proven treatments. Additionally, the “30 second” framing creates unrealistic expectations about how health and healing actually work—complex conditions don’t resolve in minutes through simple home remedies, regardless of what viral videos suggest.
The Truth About Baking Soda and Erectile Dysfunction
Let’s address the elephant in the room directly: there is absolutely no scientific evidence that baking soda, consumed as a tonic or in any other form, treats, cures, or improves erectile dysfunction. This isn’t a case of “more research needed”—it’s a case of zero credible studies supporting the claim despite extensive medical literature on both baking soda’s effects and ED treatments.

The only documented connection between sodium bicarbonate and erectile dysfunction treatment comes from a 1993 clinical study where sodium bicarbonate was added to intracavernous injection medications (drugs injected directly into the penis) to reduce injection pain by neutralizing the medication’s acidity. This is completely different from drinking baking soda as an ED treatment—it’s a buffering agent in pharmaceutical injections, not a therapeutic compound for erectile function.
Why don’t baking soda tonics help erectile dysfunction? Erectile dysfunction results from complex physiological factors including vascular insufficiency (inadequate blood flow to penile tissue due to atherosclerosis, hypertension, or endothelial dysfunction), neurological issues (nerve damage from diabetes, pelvic surgery, or spinal conditions), hormonal imbalances (low testosterone, thyroid disorders, hyperprolactinemia), psychological factors (anxiety, depression, relationship stress, performance anxiety), and medication side effects (antidepressants, blood pressure medications, certain prescription drugs). None of these root causes are addressed by alkalinity, pH changes, or the chemical properties of sodium bicarbonate.
Some viral claims suggest baking soda improves blood flow or vascular health, theoretically benefiting erectile function. However, no studies demonstrate this effect—in fact, excessive sodium intake from baking soda can worsen hypertension and cardiovascular health, potentially worsening vascular-based erectile dysfunction rather than improving it.
What Michael eventually learned (and what I teach all clients asking about “tonic for ed with baking soda”) is that effective erectile dysfunction management requires addressing actual underlying causes through proven interventions including FDA-approved medications (PDE5 inhibitors like sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil), cardiovascular optimization through diet, exercise, and weight management, blood sugar control for diabetic patients, stress management and psychological counseling when indicated, testosterone replacement therapy when deficiency is documented, and elimination of contributing medications or lifestyle factors. These evidence-based approaches work because they target root physiological mechanisms—something alkaline water simply cannot do.
What Baking Soda Tonics Actually Do
While baking soda tonics don’t treat erectile dysfunction, they do possess legitimate health-supporting properties backed by scientific research. Understanding what these tonics actually accomplish versus marketing claims helps you make informed decisions about whether they’re appropriate for your situation.

Digestive Benefits
The most well-documented benefit of baking soda water is rapid relief of acid-related digestive discomfort. Sodium bicarbonate acts as an antacid, neutralizing excess stomach acid through a chemical reaction: NaHCO₃ + HCl → NaCl + H₂O + CO₂ (sodium bicarbonate plus hydrochloric acid yields salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas). According to Mayo Clinic, sodium bicarbonate is used medically to treat heartburn and acid indigestion, though it should not replace proper medical treatment for chronic conditions.
This neutralization provides quick relief from heartburn and acid reflux symptoms (typically within 5-15 minutes), acid indigestion and sour stomach, GERD symptoms when used occasionally (not as primary treatment), and bloating related to excess stomach acid. The reaction produces carbon dioxide gas, which is why you may burp after consuming baking soda water—this is normal and indicates the chemical reaction is occurring.
However, important caveats apply: baking soda provides symptomatic relief, not treatment of underlying conditions causing excess acid, regular use can actually worsen acid production through rebound effect (stomach compensates by producing more acid), chronic GERD or reflux requires medical evaluation, not home remedies, and the high sodium content (629mg sodium per 1/4 teaspoon baking soda) makes it inappropriate for those with hypertension or sodium-restricted diets.
Alkalinity and pH Effects
Baking soda tonics temporarily increase blood pH, creating a more alkaline systemic environment. Proponents claim this alkalinity provides extensive health benefits based on “pH balance” theories, but the evidence is more nuanced than marketing suggests.
What’s scientifically supported: Your body tightly regulates blood pH (normal range 7.35-7.45), and even small deviations outside this range can be dangerous. Baking soda consumption can slightly increase blood pH and bicarbonate levels for several hours, which may provide specific performance benefits for high-intensity exercise (buffering lactic acid accumulation in muscles), temporary reduction of exercise-induced acidosis, and potential support for kidney function in certain medical contexts (some studies suggest bicarbonate supplementation may slow chronic kidney disease progression, though this requires medical supervision).
What’s not scientifically supported: claims that “acidic body” causes cancer, diabetes, or other diseases (these conditions aren’t caused by dietary pH), assertions that alkaline diet/water prevents or cures chronic diseases, and marketing suggesting pH manipulation treats conditions unrelated to acid-base balance. Your body maintains pH through sophisticated buffering systems involving lungs, kidneys, and blood chemistry—drinking alkaline water doesn’t fundamentally alter this tightly controlled homeostasis in healthy individuals.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Some research suggests alkaline environments may influence inflammatory processes, though evidence remains preliminary. A 2018 study found that drinking alkaline water with pH 8.8 may deactivate pepsin (an enzyme involved in acid reflux) and provide some buffering capacity, potentially reducing acid-related inflammation in the esophagus and throat.
However, systemic anti-inflammatory claims about “baking soda and water tonic for inflammation” significantly exceed current evidence. Chronic inflammation results from complex factors including dietary patterns (high processed foods, excess omega-6 fats, refined carbohydrates), obesity and metabolic dysfunction, sedentary lifestyle, chronic stress and poor sleep, autoimmune conditions, and environmental toxins. Simply alkalinizing with baking soda doesn’t address these root inflammatory drivers—comprehensive dietary and lifestyle optimization does.
In my clinical practice, clients experiencing chronic inflammation achieve far better results through evidence-based anti-inflammatory nutrition protocols emphasizing whole foods, omega-3 fatty acids, colorful plant compounds, and elimination of processed inflammatory triggers rather than relying on baking soda water as primary intervention.
Complete Baking Soda Tonic Recipes
If you choose to try baking soda tonics for their legitimate digestive or alkalinity benefits (not for unproven ED claims), here are safe, properly formulated recipes with variations addressing different goals.
Basic Baking Soda Tonic Recipe
Print
Basic Baking Soda Tonic Recipe
- Total Time: 30 seconds
- Yield: 1 serving (8 oz) 1x
Description
The basic 30 second hard tonic with pure baking soda provides rapid relief from heartburn and acid reflux. This simple 2-ingredient recipe takes just 30 seconds to prepare and works within 5-15 minutes for digestive discomfort. Not effective for erectile dysfunction despite viral claims.
Ingredients
1/4 teaspoon aluminum-free baking soda (Bob’s Red Mill or Arm & Hammer pure)
8 ounces (1 cup) filtered water (room temperature or slightly warm)
Instructions
1. Add 1/4 teaspoon baking soda to 8 ounces water in a glass container. Never use aluminum or reactive metal containers—use glass, stainless steel, or ceramic only.
2. Stir vigorously for 20-30 seconds until baking soda completely dissolves. No visible granules should remain in the water.
3. Drink immediately while solution is still slightly fizzy for best digestive relief results. The tonic should taste mildly salty and slightly alkaline.
Notes
Timing Guidelines: For digestive relief, consume 1-2 hours after meals when acid discomfort occurs. For general alkalinity, drink on empty stomach in morning. Never consume immediately before or during meals as it may interfere with digestion.
Maximum Frequency: No more than 1-2 servings daily, and not for extended periods (more than 2 consecutive weeks) without medical guidance. High sodium content (629mg per 1/4 tsp) makes frequent use risky.
Safety Warning: Avoid if you have hypertension, kidney disease, heart failure, or are on sodium-restricted diet. Not effective for erectile dysfunction. Consult healthcare provider before regular use.
Taste Test: If tonic tastes strongly unpleasant or overwhelmingly salty, you’ve used too much baking soda. Proper ratio creates mild, slightly alkaline taste.
- Prep Time: 30 seconds
- Cook Time: 0 minutes
- Category: Drinks
- Method: No Cook
- Cuisine: Health Tonic
Nutrition
- Serving Size: 8 oz (1 cup)
- Calories: 0
- Sugar: 0g
- Sodium: 629mg
- Fat: 0g
- Saturated Fat: 0g
- Unsaturated Fat: 0g
- Trans Fat: 0g
- Carbohydrates: 0g
- Fiber: 0g
- Protein: 0g
- Cholesterol: 0mg
Keywords: 30 second hard tonic with pure baking soda, baking soda tonic, baking soda tonic recipe, baking soda and water tonic, tonic of baking soda and water
Ingredients: 1/4 teaspoon aluminum-free baking soda (Bob’s Red Mill or Arm & Hammer pure baking soda), 8 ounces (1 cup) filtered water at room temperature or slightly warm
Instructions: Add baking soda to water in glass (never aluminum or reactive metal containers). Stir vigorously for 20-30 seconds until completely dissolved—no visible granules should remain. Drink immediately while still slightly fizzy for best results. The solution should taste mildly salty and slightly alkaline (not strongly unpleasant—if it tastes terrible, you’ve used too much baking soda).
Timing: For digestive relief, consume 1-2 hours after meals when acid discomfort occurs. For general alkalinity purposes, some protocols suggest morning consumption on empty stomach, though evidence for enhanced benefits at this timing is limited. Never consume immediately before or during meals as it may interfere with stomach acid needed for digestion.
Maximum frequency: No more than 1-2 times daily, and not for extended periods (more than 2 consecutive weeks) without medical guidance. The high sodium content and potential for metabolic alkalosis make frequent use risky.
Apple Cider Vinegar and Baking Soda Tonic
Print
Apple Cider Vinegar and Baking Soda Tonic
- Total Time: 1 minute
- Yield: 1 serving (8-10 oz) 1x
Description
Popular apple cider vinegar and baking soda tonic combines acidic ACV with alkaline baking soda, creating fizzy reaction and more neutral pH. This acv baking soda tonic provides digestive comfort with potential modest blood sugar benefits from the vinegar component.
Ingredients
1–2 tablespoons raw unfiltered apple cider vinegar (with ‘the mother’ – Bragg’s recommended)
1/4 teaspoon aluminum-free baking soda
8–10 ounces filtered water (room temperature or warm)
1 teaspoon raw honey (optional, for taste improvement)
Instructions
1. Add 1-2 tablespoons apple cider vinegar to 8-10 ounces water in a glass container. Stir to combine the vinegar and water base.
2. Add 1/4 teaspoon baking soda to the ACV water mixture. Expect VIGOROUS FIZZING as acetic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate—this is normal chemistry!
3. Stir gently and let fizzing reaction subside for 30-60 seconds. The chemical reaction produces carbon dioxide gas causing bubbles.
4. Add 1 teaspoon honey if desired for improved palatability. Stir until honey dissolves completely.
5. Drink within 5 minutes while tonic is still slightly active and fizzy. Don’t wait too long or reaction will complete.
Notes
The Chemistry Explained: Acetic acid (CH₃COOH) in vinegar reacts with sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) producing sodium acetate, water, and CO₂ gas. Final pH is approximately 6.5-7.5—more neutral than either ingredient alone.
Claims vs Reality: Provides digestive comfort and potential modest blood sugar benefits from ACV alone. Does NOT provide proven weight loss, detoxification, or ED treatment despite viral marketing claims.
ACV Quality Matters: Use raw, unfiltered apple cider vinegar containing ‘the mother’ (cloudy strands of beneficial bacteria and enzymes). Bragg’s is gold standard brand.
Cost Comparison: This variation costs approximately $0.25-$0.40 per serving versus $0.10 for basic version. Modest price increase for those who prefer ACV benefits and taste.
- Prep Time: 1 minute
- Cook Time: 0 minutes
- Category: Drinks
- Method: No Cook
- Cuisine: Health Tonic
Nutrition
- Serving Size: 8-10 oz (1 cup)
- Calories: 6
- Sugar: 0g
- Sodium: 629mg
- Fat: 0g
- Saturated Fat: 0g
- Unsaturated Fat: 0g
- Trans Fat: 0g
- Carbohydrates: 0g
- Fiber: 0g
- Protein: 0g
- Cholesterol: 0mg
Keywords: apple cider vinegar and baking soda tonic, acv baking soda tonic, apple vinegar baking soda tonic, vinegar baking soda tonic, baking soda and vinegar tonic recipe
This popular variation combines acidic apple cider vinegar with alkaline baking soda, creating a fizzy reaction and supposedly balancing pH while providing benefits of both ingredients. The apple cider vinegar and baking soda tonic remains one of the most searched variations online.
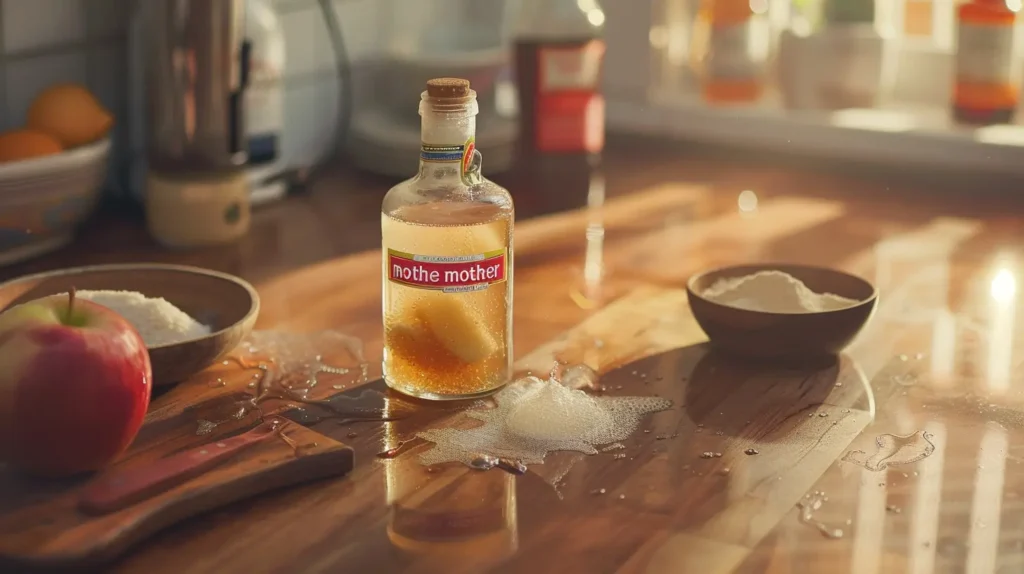

Ingredients: 1-2 tablespoons raw, unfiltered apple cider vinegar (with “the mother”), 1/4 teaspoon baking soda, 8-10 ounces water (room temperature or warm), optional: 1 teaspoon raw honey for taste
Instructions: Add apple cider vinegar to water in glass. Add baking soda—mixture will fizz vigorously as acid and base react. Stir gently and let fizzing subside (about 30-60 seconds). Add honey if desired for improved taste. Drink within 5 minutes while still slightly active.
The chemistry: Acetic acid in vinegar reacts with sodium bicarbonate: CH₃COOH + NaHCO₃ → CH₃COONa + H₂O + CO₂ (producing sodium acetate, water, and carbon dioxide gas). The final solution has more neutral pH (approximately 6.5-7.5) compared to pure baking soda water’s alkaline pH 8-8.5.
Claims versus reality: Proponents suggest this acv baking soda tonic provides digestion support, blood sugar regulation, weight loss enhancement, and detoxification benefits. Evidence shows modest blood sugar benefits from ACV alone (independent of baking soda), some digestive comfort from both ingredients, but no proven weight loss or detoxification effects beyond what proper nutrition achieves.
Baking Soda Lemon Tonic
Print
Baking Soda Lemon Tonic
- Total Time: 1 minute
- Yield: 1 serving (8 oz) 1x
Description
Refreshing baking soda lemon tonic (also called lemon baking soda tonic) substitutes fresh lemon juice for vinegar, providing vitamin C and citrus flavor. This lemon water apple cider vinegar and baking soda tonic variation offers pleasant taste with digestive relief benefits.
Ingredients
Juice of 1/2 fresh lemon (approximately 1–2 tablespoons)
1/4 teaspoon aluminum-free baking soda
8 ounces warm filtered water (not hot)
Pinch of sea salt or pink Himalayan salt (optional, for electrolytes)
Instructions
1. Squeeze juice from half a fresh lemon (approximately 1-2 tablespoons) into 8 ounces warm water. Use fresh lemon only—bottled lemon juice lacks beneficial compounds.
2. Add 1/4 teaspoon baking soda to the lemon water and stir. Mixture will fizz as citric acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate—expect moderate fizzing.
3. Wait for fizzing to subside (30-60 seconds) before proceeding. The chemical reaction will complete quickly.
4. Add pinch of sea salt or pink Himalayan salt if desired for electrolyte content. This is optional but adds mineral benefits.
5. Consume within 5-10 minutes while tonic is still slightly warm. Vitamin C degrades with time and heat exposure.
Notes
Vitamin C Benefits: Fresh lemon juice provides approximately 15-20mg vitamin C per half lemon—about 17-22% of daily recommended intake. Use immediately for maximum vitamin retention.
Palatability Advantage: Many people find lemon version more palatable than vinegar-based tonics. Citrus flavor masks alkaline taste of baking soda better than ACV.
Morning Tonic Protocol: This variation works well as morning tonic with baking soda on empty stomach. Wait 30-60 minutes before breakfast for maximum alkalinity benefits.
Fresh vs Bottled Lemon: Always use fresh-squeezed lemon juice, never bottled. Fresh lemons contain beneficial flavonoids and enzymes lost in processing and storage.
- Prep Time: 1 minute
- Cook Time: 0 minutes
- Category: Drinks
- Method: No Cook
- Cuisine: Health Tonic
Nutrition
- Serving Size: 8 oz (1 cup)
- Calories: 4
- Sugar: 0g
- Sodium: 629mg
- Fat: 0g
- Saturated Fat: 0g
- Unsaturated Fat: 0g
- Trans Fat: 0g
- Carbohydrates: 1g
- Fiber: 0g
- Protein: 0g
- Cholesterol: 0mg
Keywords: baking soda lemon tonic, lemon baking soda tonic, baking soda apple vinegar tonic, morning tonic with baking soda, lemon water apple cidder vingear and baking soda tonic
The baking soda lemon tonic or lemon baking soda tonic substitutes lemon juice for apple cider vinegar, providing vitamin C and different flavor profile while maintaining the acid-base reaction creating fizzy characteristics.
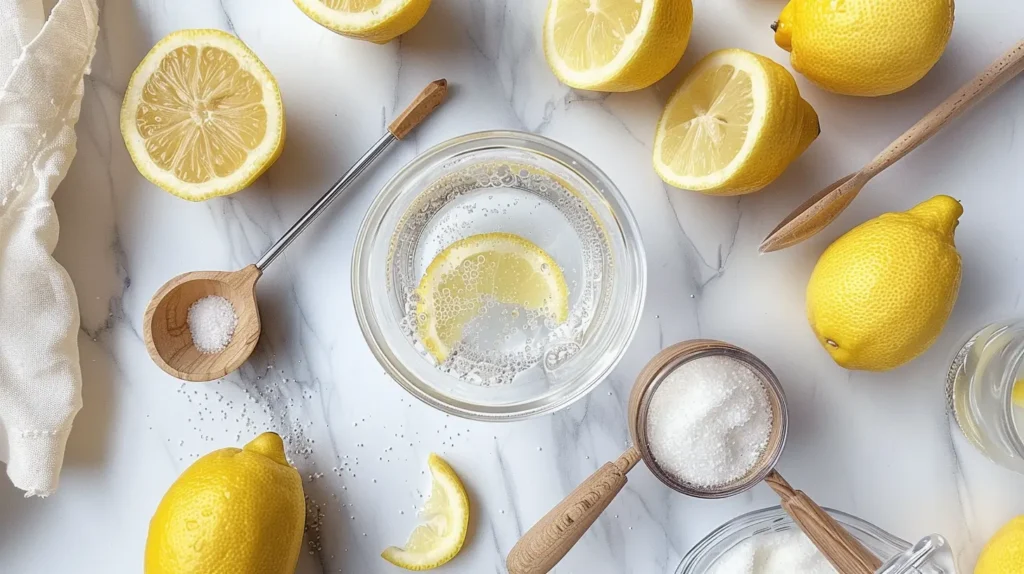

Ingredients: Juice of 1/2 fresh lemon (approximately 1-2 tablespoons), 1/4 teaspoon baking soda, 8 ounces warm water, optional: pinch of sea salt or pink Himalayan salt
Instructions: Squeeze lemon juice into water. Add baking soda and stir—mixture will fizz as citric acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate. Wait for fizzing to subside (30-60 seconds). Add optional salt if desired for electrolyte content. Consume within 5-10 minutes.
Benefits: Vitamin C from fresh lemon (approximately 15-20mg per half lemon), potentially more palatable than ACV version for those who dislike vinegar taste, and digestive relief similar to basic baking soda tonic but with added citrus flavonoids.
Comprehensive ACV Baking Soda Lemon and Manuka Honey Tonic
Print
30 Second Hard Tonic With Pure Baking Soda: Truth Revealed
- Total Time: 2 minutes
- Yield: 1 serving (8-10 oz) 1x
Description
Premium acv baking soda lemon and manuka honey tonic combines multiple functional ingredients for comprehensive wellness drink. This recipe for apple cider baking soda and water tonic represents the most complex variation with antibacterial manuka honey and optional anti-inflammatory spices.
Ingredients
1 tablespoon raw apple cider vinegar (with the mother)
Juice of 1/2 fresh lemon (1–2 tablespoons)
1/4 teaspoon aluminum-free baking soda
1 teaspoon raw manuka honey (UMF 10+ or higher recommended)
8–10 ounces warm filtered water (not hot—preserves honey enzymes)
Pinch cayenne pepper (optional, for metabolism)
Pinch turmeric powder (optional, for anti-inflammatory benefits)
Instructions
1. Add 1 tablespoon apple cider vinegar and juice of half lemon to 8-10 ounces warm (not hot) water. Stir to combine the acid base.
2. Add 1/4 teaspoon baking soda to the ACV-lemon mixture. Expect VIGOROUS FIZZING from double acid sources reacting with alkaline baking soda.
3. Stir gently and wait for fizzing to subside (60-90 seconds). The reaction will be more intense than single-acid versions due to citric acid + acetic acid.
4. Add 1 teaspoon manuka honey and stir until completely dissolved. Water must be warm (not hot) to preserve beneficial enzymes and methylglyoxal in manuka honey.
5. Add optional cayenne pepper and/or turmeric powder if using for additional functional benefits. Start with small pinch and adjust to taste tolerance.
6. Drink within 10 minutes while tonic is still slightly warm. Consume on empty stomach for maximum alkalinity and absorption benefits.
Notes
Cost Consideration: This premium version costs approximately $1.50-$2.00 per serving due to expensive manuka honey ($25-$40 per jar). Whether added cost provides proportional benefits remains debatable.
Manuka Honey Benefits: Manuka honey contains methylglyoxal (MGO) with documented antibacterial properties. UMF 10+ rating ensures minimum therapeutic MGO levels. However, benefits in this tonic format lack specific research.
Optional Spices: Cayenne provides capsaicin with modest thermogenic effects. Turmeric offers curcumin with anti-inflammatory properties (better absorbed with black pepper, though that changes taste significantly).
Best Use Case: This comprehensive tonic works best for those wanting premium ingredients and willing to invest in cost. Simpler versions provide similar digestive benefits at fraction of price.
Temperature Critical: Water must be warm but NOT hot (max 110°F/43°C) to preserve heat-sensitive enzymes in raw honey and beneficial compounds in raw ACV.
- Prep Time: 2 minutes
- Cook Time: 0 minutes
- Category: Drinks
- Method: No Cook
- Cuisine: Health Tonic
Nutrition
- Serving Size: 8-10 oz (1 cup)
- Calories: 26
- Sugar: 6g
- Sodium: 629mg
- Fat: 0g
- Saturated Fat: 0g
- Unsaturated Fat: 0g
- Trans Fat: 0g
- Carbohydrates: 7g
- Fiber: 0g
- Protein: 0g
- Cholesterol: 0mg
Keywords: acv baking soda lemon and manuka honey tonic, recipe for apple cider baking soda and water tonic, healthy diy drink tonics using baking soda, apple cider vinegar and baking soda tonic for sinus
The acv baking soda lemon and manuka honey tonic represents the most complex variation, combining multiple functional ingredients. This is the “kitchen sink” version incorporating everything enthusiasts believe provides benefits.

Ingredients: 1 tablespoon raw apple cider vinegar (with the mother), juice of 1/2 fresh lemon, 1/4 teaspoon baking soda, 1 teaspoon raw manuka honey (UMF 10+ or higher), 8-10 ounces warm water (not hot—preserves honey enzymes), optional: pinch cayenne pepper or turmeric powder
Instructions: Add ACV and lemon juice to warm water. Add baking soda—expect vigorous fizzing from double acid sources. Stir and wait for fizzing to subside (60-90 seconds). Add manuka honey and stir until dissolved. Add optional spices if using. Drink within 10 minutes while still slightly warm.
Cost consideration: This version costs approximately $1.50-$2.00 per serving due to expensive manuka honey ($25-$40 per jar), compared to $0.10-$0.25 for basic versions. Whether the added cost provides proportional additional benefits remains debatable—manuka honey does possess documented antibacterial properties from methylglyoxal content, but whether consuming it in this format provides advantages over simpler versions lacks clear evidence.
Morning Tonic With Baking Soda Protocol
Some protocols specifically emphasize timing, suggesting “morning tonic with baking soda” on empty stomach provides enhanced benefits. While timing may influence digestive effects slightly, claims about dramatically different outcomes based solely on timing exceed available evidence.
Morning protocol: Upon waking, before any food or coffee, prepare chosen baking soda tonic variation. Drink slowly over 5-10 minutes. Wait 30-60 minutes before consuming breakfast or other beverages. Proponents claim this timing maximizes alkalinity benefits and supports detoxification, though “detoxification” itself remains a poorly defined marketing term rather than specific physiological process.
Reality check: Your liver and kidneys perform continuous detoxification whether you drink morning tonics or not. While starting the day with hydration provides legitimate benefits (rehydration after overnight fast, gentle digestive stimulation), the specific alkalinity or pH effects from morning timing versus other times likely make minimal practical difference for most people.
Safety Guidelines and Contraindications
While occasional baking soda tonic consumption is generally safe for healthy adults, important safety considerations and contraindications apply that viral marketing rarely mentions.
Who Should Avoid Baking Soda Tonics
Do not consume baking soda tonics if you have: Hypertension or high blood pressure—one quarter teaspoon baking soda contains 629mg sodium (27% of 2,300mg daily limit), making it problematic for sodium-restricted diets. Kidney disease or impaired kidney function—your kidneys regulate bicarbonate levels and sodium balance; adding external sodium bicarbonate can overwhelm compromised kidneys. Heart failure or edema—high sodium content can worsen fluid retention. Alkalosis or metabolic disorders—adding alkalinity when pH is already elevated can be dangerous. Stomach ulcers or gastric conditions—while it neutralizes acid, the gas production may aggravate certain conditions.
Additionally, pregnant women should consult healthcare providers before regular baking soda consumption due to sodium load and potential pH effects. Children should not consume baking soda tonics except under specific medical guidance—their smaller bodies make proper dosing critical and risks more significant.
Proper Dosing and Frequency
Safe baking soda tonic dosing follows these parameters: maximum 1/4 to 1/2 teaspoon baking soda per serving (never exceed 1/2 teaspoon in single dose), maximum 1-2 servings per day spaced at least 4-6 hours apart, maximum 2 weeks of consecutive daily use without medical supervision (then take at least 1-2 week break), and total daily sodium bicarbonate should not exceed 1/2 to 1 teaspoon daily from all sources combined.
Exceeding these limits increases risk of: Metabolic alkalosis—dangerous elevation of blood pH causing nausea, vomiting, muscle twitching, confusion, and potentially seizures in severe cases. Sodium overload—contributing to hypertension, fluid retention, and cardiovascular stress. Milk-alkali syndrome—rare but serious condition involving high calcium levels, alkalosis, and kidney damage from excessive alkali consumption. Rebound acid hypersecretion—stomach compensates for neutralized acid by producing even more, worsening symptoms long-term.
Drug Interactions
Baking soda can interact with numerous medications by altering stomach pH and affecting drug absorption. Consult your healthcare provider before using baking soda tonics if you take: antibiotics (especially tetracyclines, quinolones—absorption reduced in alkaline environment), aspirin and NSAIDs (altered excretion rates), blood pressure medications (sodium content may counteract effects), diabetes medications (may affect blood sugar control when combined with ACV versions), thyroid medications (levothyroxine absorption impaired), and any medication requiring acidic stomach environment for proper absorption.
Always space baking soda consumption at least 2-3 hours away from medications to minimize interaction risk, though some interactions persist regardless of timing.
Signs You’re Using Too Much
Stop baking soda tonic consumption immediately and consult healthcare provider if you experience: frequent headaches or dizziness, muscle weakness or twitching, persistent nausea or vomiting, swelling in feet, ankles, or hands, increased thirst or frequent urination, confusion or mental fog, irregular heartbeat or palpitations, or worsening of digestive symptoms instead of improvement.
These symptoms may indicate metabolic alkalosis, electrolyte imbalances, or sodium overload requiring medical attention.
What Actually Works for Erectile Dysfunction
Since many people discover baking soda tonics while searching for ED solutions, let’s address what evidence-based approaches actually work—because while “ed tonic baking soda” searches may lead here, effective ED management requires different interventions.
Proven Medical Treatments
PDE5 Inhibitors (sildenafil/Viagra, tadalafil/Cialis, vardenafil/Levitra, avanafil/Stendra) remain gold standard first-line treatment for erectile dysfunction with documented efficacy in 60-70% of men. These medications work by enhancing nitric oxide signaling, improving blood flow to penile tissue. They don’t cure ED but effectively manage symptoms when underlying vascular systems are functional.
Testosterone replacement therapy when hypogonadism is documented through blood testing (total testosterone consistently below 300 ng/dL with symptoms). TRT improves erectile function in testosterone-deficient men but doesn’t help those with normal levels.
Vacuum erection devices, penile injections, intraurethral suppositories, and penile implants represent escalating interventions for cases unresponsive to oral medications.
Lifestyle and Nutritional Interventions
From my nutritionist perspective, addressing lifestyle factors provides the foundation for erectile function optimization—and unlike baking soda tonics, these interventions target actual ED mechanisms: Cardiovascular optimization through Mediterranean-style diet emphasizing vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fish, olive oil, nuts, and limiting processed foods. Erectile function is essentially a vascular health issue—what’s good for your heart is good for erectile function.
Weight loss for overweight/obese men often dramatically improves erectile function through multiple mechanisms: reduced inflammation, improved insulin sensitivity, normalized testosterone levels, improved vascular function, and enhanced self-confidence. Studies show 10% body weight loss can significantly improve erectile function scores.
Exercise, particularly aerobic activity (150+ minutes weekly) and resistance training (2-3 sessions weekly) improves vascular health, testosterone production, insulin sensitivity, and psychological wellbeing—all supporting erectile function.
Blood sugar control for diabetic patients prevents progressive nerve and vascular damage that causes ED. Maintaining HbA1c below 7% significantly reduces ED progression risk.
Stress management through mindfulness, therapy, relationship counseling, or relaxation techniques addresses psychological ED contributors that baking soda tonics cannot touch.
Michael, my patient from the opening story, ultimately achieved significant erectile function improvement not through “30 second hard tonic with pure baking soda” but through comprehensive intervention: Mediterranean-style nutrition protocol we developed together, 25-pound weight loss over 4 months, consistent exercise routine (walking plus resistance training), stress management through mindfulness practice, and appropriate medical treatment (low-dose tadalafil prescribed by his urologist). His erectile function scores improved from severe (IIEF-5 score 8) to mild (IIEF-5 score 18) within 5 months—real results from addressing real mechanisms, not from viral remedies lacking scientific basis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of drinking baking soda tonic?
Evidence-supported benefits of drinking baking soda tonic include rapid relief from heartburn and acid reflux through acid neutralization (typically within 5-15 minutes), temporary increase in blood alkalinity that may buffer lactic acid during high-intensity exercise potentially improving athletic performance, and relief from acid indigestion and sour stomach symptoms. Some preliminary research suggests potential kidney health support in chronic kidney disease patients, though this requires medical supervision rather than self-treatment.
However, baking soda tonic benefits do NOT include erectile dysfunction treatment, sexual performance enhancement, significant weight loss, detoxification (your liver and kidneys handle this naturally), disease prevention or cure, or metabolic “boosting” beyond temporary pH changes. Most dramatic health claims circulating on social media lack scientific support—stick with documented benefits (primarily digestive relief) when considering whether baking soda tonics are appropriate for you.
What happens if you take apple cider vinegar and baking soda together?
When you combine apple cider vinegar and baking soda together, a chemical reaction occurs: acetic acid in the vinegar reacts with sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) producing sodium acetate, water, and carbon dioxide gas. This creates the characteristic fizzing and bubbling you observe when mixing these ingredients.
The final mixture has more neutral pH (approximately 6.5-7.5) compared to acidic vinegar alone (pH 2.5-3.5) or alkaline baking soda water (pH 8-8.5). Some proponents claim this “pH balanced” combination provides superior benefits, but evidence is limited. You essentially get modest digestive benefits from the acid neutralization, potential small blood sugar benefits from the apple cider vinegar component (independent of the baking soda), improved palatability compared to drinking straight vinegar, and vigorous fizzy texture some find pleasant.
However, you do NOT get enhanced weight loss, erectile function improvement, detoxification, or disease prevention beyond what proper nutrition provides. The apple cider vinegar and baking soda tonic remains popular partly because the fizzy reaction creates perception of chemical “activity” translating to biological benefit—but reactions in glass don’t necessarily translate to reactions in your body providing meaningful health advantages.
What is the fastest way to solve erectile dysfunction?
The fastest way to address erectile dysfunction symptoms (not cure, but manage) is consulting a healthcare provider who can prescribe FDA-approved PDE5 inhibitor medications (sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil, avanafil). These medications work within 30-60 minutes when taken as needed, providing effective symptom management for 60-70% of men with ED.
However, “fastest” doesn’t mean “best”—comprehensive ED management requires identifying and addressing underlying causes including cardiovascular disease screening and optimization, diabetes or blood sugar dysregulation management, hormonal evaluation (especially testosterone levels), psychological factors assessment, medication review (many drugs cause or worsen ED), and lifestyle factor modification including weight loss, exercise, smoking cessation, and alcohol moderation.
Home remedies like “30 second hard tonic with pure baking soda” or other viral ED tonics are NOT the fastest or any way to solve erectile dysfunction—they simply don’t work for this purpose regardless of marketing claims. They may delay proper medical evaluation and evidence-based treatment, potentially allowing underlying conditions like cardiovascular disease or diabetes to progress untreated. Always consult qualified healthcare providers for ED evaluation rather than relying on unproven home remedies, regardless of how compelling viral videos make them seem.
How do you make a baking soda tonic?
To make a basic baking soda tonic: Add 1/4 teaspoon aluminum-free baking soda to 8 ounces (1 cup) room temperature or warm filtered water in a glass container (never aluminum). Stir vigorously for 20-30 seconds until baking soda completely dissolves with no visible granules remaining. Drink immediately while solution is still slightly fizzy. The tonic should taste mildly salty and slightly alkaline—if it tastes strongly unpleasant, you’ve used too much baking soda.
For variations, you can make apple cider vinegar baking soda tonic by adding 1-2 tablespoons raw ACV before the baking soda (expect vigorous fizzing), baking soda lemon tonic using juice of half lemon instead of or in addition to ACV, or comprehensive versions adding manuka honey, cayenne, or turmeric for additional flavor and functional compounds. Regardless of variation, core safety guidelines apply: maximum 1/4 to 1/2 teaspoon baking soda per serving, no more than 1-2 servings daily, consume 1-2 hours after meals or on empty stomach (never immediately before/during meals), and don’t use continuously for more than 2 weeks without medical guidance.
What is the best natural drink for erectile dysfunction?
There is no “best natural drink” that treats erectile dysfunction—ED is a complex medical condition requiring addressing underlying physiological causes rather than consuming specific beverages. However, certain drinks support overall vascular and metabolic health that indirectly benefits erectile function as part of comprehensive lifestyle optimization.
Drinks that support vascular health relevant to erectile function include: Beet juice containing dietary nitrates that convert to nitric oxide, the same compound PDE5 inhibitors enhance—studies show 2-3 cups daily may modestly improve vascular function and blood pressure. Pomegranate juice rich in antioxidants and polyphenols that support endothelial function—some small studies suggest regular consumption may provide modest ED benefit in mild cases. Green tea containing catechins with vascular-protective properties—consistent consumption supports overall cardiovascular health. Water—adequate hydration maintains blood volume and cardiovascular function; chronic dehydration can impair erectile function.
However, none of these drinks “cure” erectile dysfunction, and effects are modest at best, requiring consistent consumption over weeks to months as part of comprehensive healthy lifestyle. They work through supporting vascular health generally, not through specific erectile mechanisms. Baking soda tonics don’t make this list because they provide no documented vascular or erectile benefits despite viral marketing suggesting otherwise.
Do baking soda and water reduce belly fat?
No, baking soda and water do not reduce belly fat. This viral claim lacks any scientific evidence—fat loss requires sustained caloric deficit created through consuming fewer calories than you expend, and no amount of baking soda water changes this fundamental energy balance equation.
The origin of this myth likely stems from: temporary reduction in bloating from improved digestion (mistaken for fat loss), water weight fluctuations from sodium effects (not fat loss), and marketing conflating “detoxification” or “alkalinity” with fat reduction (these don’t correlate). Some people report feeling less bloated after baking soda tonics due to improved digestion or gas relief—this is water weight and gas, not fat loss.
Actual belly fat reduction requires comprehensive approach including: caloric deficit of 300-500 calories daily from maintenance level, emphasis on whole foods with high satiety (vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, healthy fats), regular physical activity combining cardio (150+ minutes weekly) and resistance training (2-3 sessions weekly) to maintain muscle mass during fat loss, adequate sleep (7-9 hours nightly) supporting hormones that regulate fat metabolism, and stress management preventing cortisol-driven abdominal fat accumulation.
If baking soda tonics fit into a comprehensive weight loss nutrition protocol you’re following for other reasons (digestive comfort, for example), they won’t harm your progress—but they also won’t accelerate fat loss or specifically target belly fat regardless of viral claims suggesting otherwise.
What not to mix with baking soda?
Several substances should not be mixed with baking soda due to safety concerns or drug interactions: Aluminum containers or utensils—baking soda can react with aluminum, potentially leaching aluminum into your tonic and affecting taste. Use glass, stainless steel, or ceramic containers only.
Alcohol—combining baking soda with alcohol increases risk of stomach upset and may mask intoxication effects while potentially enhancing alcohol’s negative impacts on stomach lining. Calcium supplements or calcium-rich beverages—excessive alkali plus high calcium can contribute to milk-alkali syndrome in susceptible individuals, though this requires substantial quantities. Medications requiring acidic stomach—baking soda neutralizes stomach acid potentially impairing absorption of numerous medications including antibiotics, thyroid medications, certain antifungals, and various other drugs. Always space baking soda 2-3 hours away from medications.
Very hot liquids—baking soda in very hot water can create unexpectedly vigorous reaction, potentially causing burns or scalding. Use room temperature or moderately warm water only. Excess quantities—never use more than 1/2 teaspoon baking soda in single serving or exceed 1 teaspoon daily total from all sources combined without medical supervision.
Is it safe to drink baking soda water daily?
Drinking baking soda water daily for SHORT periods (1-2 weeks maximum) is generally safe for healthy adults without contraindications when using appropriate amounts (1/4 to 1/2 teaspoon baking soda in 8 ounces water, maximum 1-2 servings daily). However, long-term daily consumption poses several risks.
Risks of daily baking soda water consumption include: Metabolic alkalosis—chronic alkalinity can disturb normal body pH regulation, causing symptoms from mild (nausea, fatigue) to severe (confusion, seizures, cardiac arrhythmias). Sodium overload—each 1/4 teaspoon provides 629mg sodium (27% of 2,300mg daily limit), contributing to hypertension, cardiovascular stress, and fluid retention when consumed daily. Nutrient malabsorption—chronic acid neutralization impairs mineral absorption including iron, calcium, magnesium, and vitamin B12, potentially causing deficiencies over months. Rebound acid hypersecretion—stomach compensates for regularly neutralized acid by producing even more, worsening acid-related symptoms long-term. Kidney stress—chronic sodium bicarbonate consumption increases workload on kidneys regulating pH and sodium balance.
Safer approach: use baking soda water occasionally for acute digestive relief (2-3 times weekly maximum), take regular breaks (use for 1-2 weeks, then discontinue for 1-2 weeks), address underlying causes of chronic acid reflux or digestive issues rather than masking symptoms indefinitely, and consult healthcare provider if you feel you need daily acid relief—chronic symptoms warrant medical evaluation, not ongoing self-treatment.
Can you drink baking soda and apple cider vinegar to lose weight?
While you can safely drink baking soda and apple cider vinegar together (they won’t harm you in appropriate amounts), this combination does not cause weight loss beyond what proper caloric deficit achieves. The viral weight loss claims surrounding this mixture lack scientific support.
Some limited evidence suggests apple cider vinegar alone (independent of baking soda) may provide very modest benefits: small improvement in satiety potentially reducing caloric intake by 50-100 calories per meal in some studies, minor blood sugar stabilization that may reduce cravings, and possible slight enhancement of fat oxidation during exercise (effect size small and inconsistent across studies). However, these potential ACV benefits are modest (typically 1-2 pounds additional loss over 12 weeks compared to placebo in studies), occur independent of baking soda addition, and pale compared to comprehensive nutrition and lifestyle optimization.
The baking soda component provides no weight loss benefit—it simply neutralizes the vinegar’s acidity, potentially reducing the already-small benefits ACV alone might offer. If you enjoy the taste and digestive comfort of baking soda and apple cider vinegar mixture and it helps you stay hydrated or feel satisfied, there’s no harm including it in a comprehensive weight loss protocol—but don’t expect it to drive meaningful fat loss. Actual weight loss requires sustained caloric deficit through balanced nutrition emphasizing whole foods, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management—not from alkaline tonics or vinegar drinks regardless of social media popularity.
Is baking soda good for heartburn while pregnant?
Baking soda provides effective heartburn relief, but pregnant women should exercise caution and consult healthcare providers before regular use due to several pregnancy-specific concerns.
Concerns about baking soda during pregnancy include: Sodium load—pregnancy already increases blood volume and cardiovascular demand; additional sodium from baking soda may contribute to swelling, elevated blood pressure, or preeclampsia risk in susceptible women. Fluid retention—high sodium can worsen the edema many pregnant women experience, particularly in third trimester. Metabolic effects—pregnancy involves significant metabolic and pH changes; adding external alkalinity may disrupt these normal adaptations. Nutrient absorption—chronic acid neutralization can impair mineral absorption at a time when nutrient needs are elevated for fetal development.
Safer heartburn management during pregnancy includes: Dietary modifications—small frequent meals, avoiding trigger foods (spicy, fatty, acidic), not eating within 2-3 hours of bedtime. Positioning—elevating head of bed 6-8 inches, sleeping on left side, avoiding lying down immediately after eating. Pregnancy-safe antacids—calcium carbonate products (Tums) generally considered safer than sodium bicarbonate during pregnancy; magnesium-based antacids may also be appropriate. Medical consultation—persistent heartburn during pregnancy warrants discussion with OB/GYN or midwife who can recommend appropriate interventions and rule out complications.
Occasional baking soda use for acute relief is unlikely to harm pregnancy, but regular daily consumption should be avoided without medical guidance due to sodium content and pH effects. Always prioritize lifestyle modifications and pregnancy-safe alternatives first, reserving baking soda for occasional use only if approved by your healthcare provider.
How long does it take for baking soda to reduce inflammation?
The timeframe for baking soda to reduce inflammation remains unclear because robust scientific evidence supporting systemic anti-inflammatory effects from drinking baking soda water is limited. Most “baking soda and water tonic for inflammation” claims extrapolate from preliminary research or mechanisms that don’t necessarily translate to meaningful clinical anti-inflammatory benefits.
What we know: Baking soda water creates temporary alkalinity in blood and tissues (within 30-60 minutes of consumption, lasting several hours). Some research in animals and test tubes suggests alkaline environments may reduce certain inflammatory markers. A 2018 study published in Journal of Immunology found that oral sodium bicarbonate may signal anti-inflammatory pathways through effects on mesothelial cells and splenic macrophages—but this research was preliminary and conducted primarily in rats, not humans with inflammatory conditions.
What we don’t know: Whether drinking baking soda water provides clinically meaningful reduction in systemic inflammation in humans, what dose and duration would be required for any potential effect, how long any effects might last, and whether benefits (if they exist) outweigh risks of long-term sodium bicarbonate consumption.
More effective inflammation reduction strategies with strong evidence include: Dietary pattern changes emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods (omega-3 fatty acids, colorful plant compounds, fermented foods) and eliminating pro-inflammatory processed foods, refined carbohydrates, and excess omega-6 oils—expect noticeable improvements within 2-4 weeks, substantial changes within 2-3 months. Weight loss for overweight individuals—fat tissue produces inflammatory compounds; losing 10% body weight often significantly reduces inflammatory markers within 3-4 months. Exercise—regular physical activity (150+ minutes weekly) reduces systemic inflammation with benefits emerging within 4-6 weeks of consistent activity.
If you’re dealing with chronic inflammation causing symptoms affecting quality of life, focus on evidence-based interventions with proven anti-inflammatory effects rather than unproven tonics. Baking soda water won’t harm inflammation reduction efforts if used occasionally for digestive comfort, but don’t rely on it as primary anti-inflammatory strategy when far more effective approaches exist.
What do baking soda and water do for your kidneys?
Baking soda’s relationship with kidney health is complex—emerging research suggests potential benefits in specific kidney disease contexts, but self-treatment without medical supervision is inappropriate and potentially dangerous.
Potential kidney benefits (under medical supervision only): Some studies suggest sodium bicarbonate supplementation may slow progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in patients with metabolic acidosis (common complication of advanced kidney disease where kidneys can’t regulate pH effectively). A 2009 study published in Journal of American Society of Nephrology found that oral sodium bicarbonate supplementation slowed decline in kidney function and reduced risk of developing end-stage kidney disease in CKD patients with metabolic acidosis. Mechanisms may involve: reducing acid load on already-compromised kidneys, preserving remaining kidney function, potentially slowing protein breakdown and muscle wasting associated with kidney disease acidosis.
However, critical caveats apply: these potential benefits apply specifically to CKD patients with documented metabolic acidosis under medical supervision—NOT healthy individuals drinking baking soda tonics preventatively. Kidney disease patients require precise sodium bicarbonate dosing based on lab values and kidney function—self-dosing is inappropriate and dangerous. Excessive sodium bicarbonate can actually harm kidneys, particularly in people with kidney disease who have impaired ability to excrete sodium. Some kidney conditions contraindicate sodium bicarbonate use due to sodium content and pH effects.
For kidney health in general population (no kidney disease): Stay well-hydrated with plain water (adequate fluid supports kidney function). Maintain healthy blood pressure and blood sugar (primary causes of kidney disease). Limit sodium from all sources including processed foods. Avoid excessive protein intake (more than 2g per kg body weight daily). Don’t use baking soda tonics preventatively for “kidney health”—healthy kidneys regulate pH beautifully without external alkalinity, and excess sodium from baking soda may stress rather than support kidney function over time.
If you have kidney disease or impaired kidney function, never self-treat with baking soda tonics—work with nephrologist who can determine if sodium bicarbonate is appropriate and prescribe proper medical-grade formulations at correct dosing based on your specific kidney function and lab values.
Making Informed Choices About Viral Health Trends
Remember Michael from the beginning of this article—the patient who’d been mixing baking soda water for two weeks hoping to cure erectile dysfunction based on viral videos? After our comprehensive consultation reviewing the actual science (or lack thereof) behind ED claims, understanding legitimate baking soda benefits for digestion, and developing evidence-based nutrition and lifestyle protocol addressing his actual health concerns, Michael made remarkable progress.
Six months later, Michael reports: “I’m embarrassed I fell for the 30 second hard tonic hype, but I’m grateful it led me to your office where I learned what actually works. The 25 pounds I’ve lost through proper nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and appropriate medical treatment from my doctor achieved what no tonic ever could—real improvement in erectile function, energy, confidence, and overall health. I occasionally use baking soda water for heartburn after spicy meals, which is what it’s actually good for, but I’m no longer looking for miracle cures in viral videos.”
Michael’s experience illustrates a crucial lesson about viral health trends including the “30 second hard tonic with pure baking soda”: evaluate claims skeptically by asking what specific health mechanisms does this intervention target? Are the proposed benefits physiologically plausible based on known biology? What does peer-reviewed scientific literature say versus social media marketing? Who profits from promoting this trend and what are their credentials/conflicts of interest? What are potential risks and contraindications rarely mentioned in promotional content?
Apply this critical thinking to any trending remedy whether it’s baking soda tonics, apple cider vinegar protocols, detox cleanses, or other viral health interventions. Some contain kernels of truth wrapped in exaggeration—baking soda tonics genuinely help acid reflux but don’t cure erectile dysfunction. Others are purely marketing without physiological basis.
In my 15+ years as chef nutritionist, I’ve observed that lasting health improvements come not from “30 second” interventions but from sustained commitment to evidence-based fundamentals: nutrient-dense whole foods emphasizing vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, regular physical activity combining cardiovascular and resistance training, adequate sleep prioritizing 7-9 hours nightly, stress management through whatever techniques resonate with you, strong social connections and supportive relationships, and appropriate medical care when conditions require professional intervention.
These fundamentals aren’t sexy or viral-worthy—they can’t be condensed into “30 second” solutions or marketed with shocking claims. But they work consistently, sustainably, and safely in ways no tonic ever will. Whether you’re dealing with erectile dysfunction, chronic inflammation, weight management challenges, or other health concerns, start with evidence-based foundations before exploring adjunct interventions like baking soda tonics for their legitimate limited benefits.
About Chef Peter
Chef Peter is a certified chef nutritionist with over 15 years of experience specializing in therapeutic nutrition, metabolic health optimization, and evidence-based dietary interventions. His unique background combines culinary expertise with rigorous nutritional science, allowing him to separate viral health trends from legitimate evidence-based practices. Peter has worked with thousands of clients navigating confusing health claims, helping them understand what actually works versus marketing hype. He’s particularly passionate about debunking misleading viral remedies while identifying kernels of truth they may contain and directing clients toward proven interventions. When not consulting with clients, Peter researches emerging nutrition science, develops therapeutic recipes, and teaches culinary medicine principles. He believes in empowering people with knowledge to make informed health decisions rather than falling prey to sensational but unsubstantiated claims flooding social media.
💡 Chef Peter’s Quick Tip
Question Viral Claims with These 5 Filters: Before trying any trending health remedy like the “30 second hard tonic with pure baking soda,” ask yourself: (1) Is there peer-reviewed scientific evidence, or just testimonials and marketing? (2) Does the claim sound too good to be true (curing complex conditions in 30 seconds)? (3) Who’s promoting this and what do they sell? (4) What are the risks and contraindications not mentioned? (5) Does it address actual physiological mechanisms of my condition? Most viral remedies fail multiple filters. Baking soda tonics pass filter 1 for digestive relief but fail for ED claims. When claims don’t pass these filters, focus energy on evidence-based interventions with your healthcare team instead. Save yourself time, money, and disappointment by evaluating critically before experimenting—your health deserves better than TikTok-level “research.”
📢 Share This Article
Found this evidence-based analysis of the “30 second hard tonic with pure baking soda” helpful? Share it with friends, family, or online communities asking about this viral remedy. Help others separate fact from fiction by sharing accurate information about what baking soda tonics actually do versus exaggerated marketing claims. Use the share buttons below to post on social media, or send directly to anyone considering trying these tonics. Knowledge empowers better health decisions—help combat misleading viral health trends by spreading evidence-based information instead of sensational but unsubstantiated claims.
⚠️ Medical Disclaimer
This article provides educational information about baking soda tonics and is not medical advice. Baking soda consumption carries risks including metabolic alkalosis, sodium overload, drug interactions, and complications for certain medical conditions. Never use baking soda tonics as treatment for erectile dysfunction or other serious medical conditions—these require professional medical evaluation and evidence-based treatment. Always consult qualified healthcare providers including physicians, registered dietitians, or specialists before starting any new dietary supplement or health protocol, especially if you have hypertension, kidney disease, heart conditions, or take medications. Individual responses vary based on health status, medications, and underlying conditions. Information presented reflects current understanding as of December 2025 but may change as research evolves. Chef Peter is a certified nutritionist, not a medical doctor, and provides nutritional education—not medical diagnosis or treatment. If you experience symptoms requiring medical attention, contact healthcare providers immediately rather than relying on home remedies. This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment recommendations.













